NEWS 2016
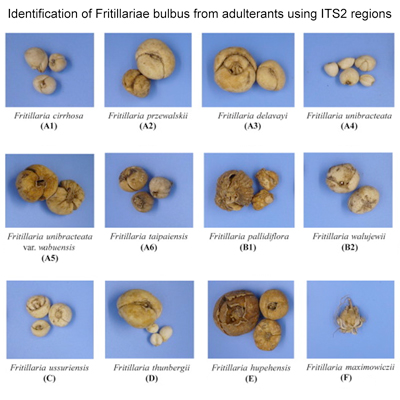
Identification of Fritillariae bulbus from adulterants using ITS2 regions
Li Xiang¹, Yanyan Su², Xiwen Li¹, Gang Xue³, Qiang Wang³, Julian Shi³, Lizhi Wang⁴, Shilin Chen¹
Plant Gene (2016)
doi: 10.1016/j.plgene.2016.05.001
¹Institute of Chinese Materia Medica, China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100700, China
²Huaibei Normal University, Anhui 235000, China
³Chengdu enwei investment (group) co., ltd., Chendu, 610200, China
⁴College of Traditional Chinese Pharmacy, Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 300193, China
Abstract
Distinguishing the five types of Fritillariae bulbus (Fritillariae cirrhosae bulbus, Fritillariae ussuriensis bulbus, Fritillariae pallidiflorae bulbus, Fritillariae thunbergii bulbus and Fritillariae hupehensis bulbus) is difficult because of their similar morphological, physical, and chemical characteristics. These species, which are included in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia, exhibit different therapeutic effects. Therefore, we used internal transcribed spacer 2 (ITS2) regions as DNA barcode to distinguish the five types of Fritillariae bulbus from each other and their adulterants. A total of 151 samples belonging to five types of Fritillariae bulbus (a total of 11 species of Fritillaria) and two adulterant species were collected. The phylogeny was constructed using the neighbor joining (NJ), maximum parsimony (MP), and maximum likelihood (ML) methods. Genomic DNAs were successfully extracted from all bulbus samples and obtaining high-quality ITS2 sequences via polymerase chain reaction optimization. The length of the ITS2 sequence of 12 Fritillaria species ranged from 235 bp to 241 bp, and the average GC content was over 68%. Adulterants Bolbostemma paniculatum and F. maximowiczii could be distinguished from all Fritillariae bulbus species by using the distance and tree methods. The ML tree showed better topology than the NJ and MP trees. Members of each type of Fritillariae bulbus formed one clade, which was strongly supported with bootstrap values, except for Fritillariae thunbergii bulbus and Fritillariae hupehensis bulbus in the ML tree. Therefore, DNA barcoding technology based on ITS2 regions can be used to distinguish the five types of Fritillariae bulbus from each other and their adulterants except for Fritillariae thunbergii bulbus and Fritillariae hupehensis bulbus.